BAY-069, a Novel (Trifluoromethyl)pyrimidinedione-Based BCAT1/2 Inhibitor and Chemical Probe.
Gunther, J., Hillig, R.C., Zimmermann, K., Kaulfuss, S., Lemos, C., Nguyen, D., Rehwinkel, H., Habgood, M., Lechner, C., Neuhaus, R., Ganzer, U., Drewes, M., Chai, J., Bouche, L.(2022) J Med Chem 65: 14366-14390
- PubMed: 36261130
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00441
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7NTR, 7NWA, 7NWB, 7NWC, 7NWE, 7NWM, 7NXN, 7NXO, 7NY2, 7NY9, 7NYA - PubMed Abstract:
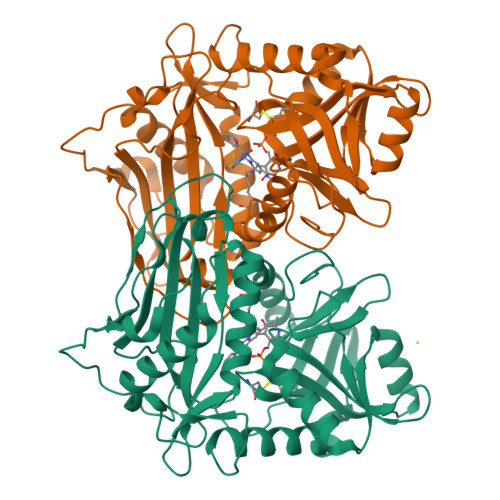
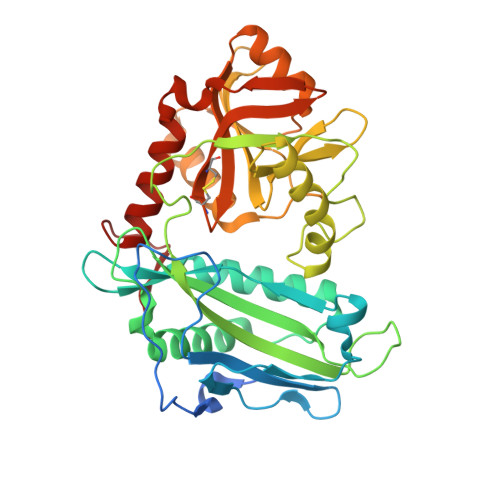
The branched-chain amino acid transaminases (BCATs) are enzymes that catalyze the first reaction of catabolism of the essential branched-chain amino acids to branched-chain keto acids to form glutamate. They are known to play a key role in different cancer types. Here, we report a new structural class of BCAT1/2 inhibitors, (trifluoromethyl)pyrimidinediones, identified by a high-throughput screening campaign and subsequent optimization guided by a series of X-ray crystal structures. Our potent dual BCAT1/2 inhibitor BAY-069 displays high cellular activity and very good selectivity. Along with a negative control (BAY-771), BAY-069 was donated as a chemical probe to the Structural Genomics Consortium.
Organizational Affiliation:
Research & Development, Pharmaceuticals, Bayer Pharma AG, Müllerstrasse 178, 13353Berlin, Germany.